Selected Publications
プレスリリース1 神戸大学 Research at Kobe サイト
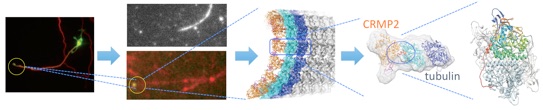
/構造生物学的手法と細胞生物学的手法を融合し、原子から個体レベルまでスケールが異なる階層で同一の分子の構造・機能を追う「シームレス構造生物学」を実践した報告である。題材は微小管結合蛋白質CRMP2で、CRMP2の微小管ダイナミクス制御を通じた軸索伸長制御作用に着目し、CRMP2が軸索型微小管の重合を促す事により効率良く軸索を伸ばすことを解明した。
Wang D, Nitta R, Morikawa M, Yajima H, Inoue S, Shigematsu H, Kikkawa M, Hirokawa N.
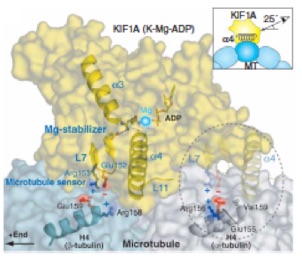
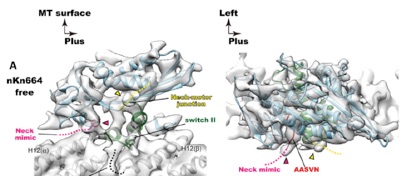
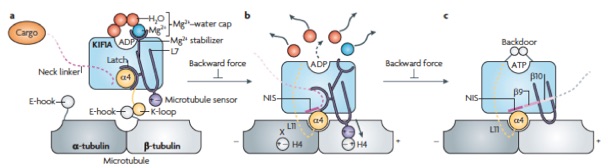
/キネシン型モーターKIF19Aは微小管上を一方向性に動き、端まで到達すると微小管を脱重合する二刀流キネシンである。KIF19Aは線毛の長さを適切に保ち、その異常は不妊や脳室拡大、易感染性などを呈する。本論文では、KIF19Aが2つの異なる機能を達成するための構造基盤を解明した。KIF19Aの微小管結合部位にサスペンションに似たあそびを作ることで、微小管のどの部分にも結合できるように調整されていた。
Yamagishi M, Shigematsu H, Yokoyama T, Kikkawa M, Sugawa M, Aoki M, Shirouzu M, Yajima J, Nitta R.
Morikawa M, Yajima H, Nitta R, Inoue S, Ogura T, Sato C, Hirokawa N.
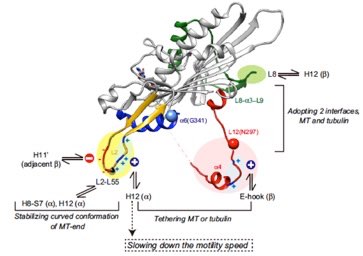
/キネシン型モーターKIF5は、神経細胞軸索突起に特有の形態を持つ微小管を道標として、多数の樹上突起の中から軸索突起のみに進入する。本論文では、クライオ電子顕微鏡解析によりKIF5と軸索型微小管の複合体の構造を明らかにし、KIF5の道標の構造基盤を解明した。また、KIF5の結合が微小管の構造変化を誘起し、KIF5が結合しやすい形態へ変わることも示した。
Yamashita M, Nitta E* and Suda T.*
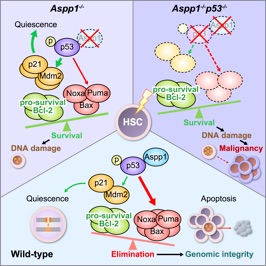
/造血幹細胞は細胞周期の静止期にあり、遺伝子変異から守られる一方で、修復が困難で変異を蓄積しやすいというジレンマを抱えている。本論文ではがん抑制遺伝子p53とアポトーシス関連因子Aspp1が協調して損傷を負った細胞にアポトーシスを誘導して造血幹細胞プールの健全性を維持していることを示し、造血幹細胞が自ら腫瘍を抑制する機構を持つことを証明した。
Chang Q, Nitta R, Inoue S, Hirokawa N.
Structural Basis for the ATP-induced Isomerization of Kinesin. J. Mol. Biol. 2013 425:1869-80.
/キネシン型分子モーターKIF4は、染色体の紡錘糸微小管のダイナミクスを止めて微小管を安定化するという特異な働きを持つ分子である。本論文ではその結晶構造を初めて報告し、変異体の解析も並行して行うことで、微小管のダイナミクスに重要なアミノ酸を特定した。その阻害剤は、染色体分裂を制御する可能性があり、抗がん剤などの創薬への応用も視野に入る。
Yajima H., Ogura T, Nitta R, Okada Y, Sato C, Hirokawa N.
/本論文では、重合期微小管のクライオ電子顕微鏡構造を世界で初めて明らかにし、微小管が重合・脱重合を繰り返す性質(動的不安定性)の構造基盤を解明した。微小管の構成分子チュブリンの、キネシンにも似た大きな構造変化を捉えた。動的不安定性は、細胞の極性形成や細胞分裂など、生命の根幹に関わる現象を牽引している性質であり、神経細胞成熟過程の分子機構解明など重要な生命現象理解への足がかりとなる成果である。
/キネシン型分子モーター全般に通じる動作機構について独自のモデルを提唱した。キネシンは、ATPポケットで起こる小さな構造変化を微小管結合部位の大きな構造変化へと増幅し、(1)微小管に沿った一次元ブラウン運動、(2)前方に移動しながら微小管へ結合する、(3)微小管から能動的に解離する、の3状態を遷移する。(2)の過程において確率的に前進する(ブラウンーラチェット機構)。
/2004年にScience誌に発表した論文の続報でキネシン型分子モーターKIF1AのADP放出過程の構造変化を、X線結晶解析を用いて捉えた。これにより、キネシンの加水分解サイクルの構造変化の全貌を世界で初めて明らかにした。前作ではキネシンの微小管脱着の分子機構を、本論文では運動方向性決定の構造基盤を明らかにした。つまりキネシンは、ADP放出過程で前後方向に非対称な微小管結合面を作り、確率的に前へ結合しやすくすることで前進している。
Ogawa T, Nitta R, Okada Y, Hirokawa N.
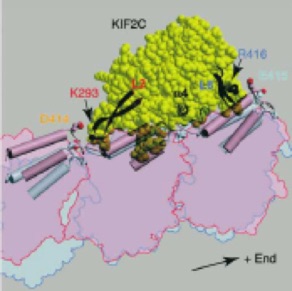
/微小管を壊す(脱重合する)ことに特化したキネシン型分子モーターKIF2Cは、細胞分裂を牽引する重要な分子である。本論文では、世界で初めてKIF2Cの結晶構造を解明し、KIF2Cの微小管脱重合機構の構造基盤を明らかにした。これによると、KIF2Cは微小管壁よりも両端に結合しやすい特性を有し、KIF2Cの微小管両端への結合が、微小管を脱重合しやすい形態へと構造変化させていることが明らかになった。
Nitta R, Kikkawa M, Okada Y, Hirokawa N.
/キネシン型分子モーターがATPを加水分解する際の構造変化を、X線結晶解析を用いて世界で初めて捉えることに成功した。これによるとキネシンは、共通の祖先を持つとされる低分子量GTPアーゼと非常に類似したエネルギー変換機構を用いていることがわかった。つまりキネシンの動作の本質は、ATPの加水分解エネルギーを利用して、エフェクター分子である微小管との結合・解離を繰り返すことであることが明らかになった。
Full Publications
2018
-
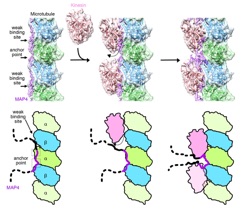
Shima T, Morikawa M, Kaneshiro J, Kambara T, Kamimura S, Yagi T, Iwamoto H, Uemura S, Shigematsu H, Shirouzu M, Ichimura T, Watanabe TM, Nitta R, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. Kinesin-binding-triggered conformation switching of microtubules contributes to polarized transport. J Cell Biol. 2018 Oct 8. pii: jcb.201711178.
-
Shigematsu H, Imasaki T, Doki C, Sumi T, Aoki M, Kamo TU, Sakamoto A, Tokuraku K, Shirouzu M, Nitta R. Structural insight into microtubule stabilization and kinesin inhibition by Tau-family MAPs. J. Cell Biol. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201711182
-
仁田 亮. キネシンスーパーファミリータンパク質の多様な機能を支える分子構造基盤. 顕微鏡(解説), 53巻2号
-
Nitta R, Imasaki T, Nitta E. Recent Progress of Structural Biology: Lessons from Our Research History. Microscopy, 2018, 1–9 doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfy022.
-
仁田 亮.実験医学(2018年5月号)クライオ電子顕微鏡による構造解析が拓く次世代の生命科学・創薬.X線とクライオ電顕で微小管モーターの動きに迫る.X-ray and cryo-EM visualize the motility of microtubule-based motors. 羊土社 Vol.36 No.8,PP.1323-1327.
-

-
Sumi T, Imasaki T, Aoki M, Sakai N, Nitta E, Shirouzu M, & Nitta R. Structural Insights into the Altering Function of CRMP2 by Phosphorylation. Cell Struct. Funct. 43:15-23. doi: 10.1247/csf.17025, 2018.
-
Imasaki T, Wenzel S, Yamada K, Bryant ML, Takagi Y. Titer estimation for quality control (TEQC) method: A practical approach for optimal production of protein complexes using the baculovirus expression vector system. PLOS ONE 13: e0195356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195356. eCollection 2018.
2017
-
Niwa S, Nakamura F, Tomabechi Y, Aoki M, Shigematsu H, Matsumoto T, Yamagata A, Fukai S, Hirokawa N, Goshima Y, Shirouzu M, Nitta R. Structural basis for CRMP2-induced axonal microtubule formation. Sci. Rep. 7: 10681. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11031-4, 2017.
-
Rogers CM, Wang JC, Noguchi H, Imasaki T, Takagi Y, Bochman ML. Yeast Hrq1 shares structural and functional homology with the disease-linked human RecQ4 helicase. Nucleic Acids Research 45, 5217–5230. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx151. 2017
-
2016
-
Wang D, Nitta R, Morikawa M, Yajima H, Inoue S, Shigematsu H, Kikkawa M, Hirokawa N. Motility and Microtubule Depolymerization Mechanisms of the Kinesin-8 motor, KIF19A. ELife 2016 pii: e18101. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18101.
-
Yamagishi M, Shigematsu H, Yokoyama T, Kikkawa M, Sugawa M, Aoki M, Shirouzu M, Yajima J, Nitta R. Structural basis of backwards motion in kinesin-1–kinesin-14 chimera: implication for kinesin-14 motility. Structure 2016 24;1322-34.
-
Koide S, Oshima M, Takubo K, Yamazaki S, Nitta E, Saraya A, Aoyama K, Kato Y, Miyagi S, Nakajima-Takagi Y, Chiba T, Matsui H, Arai F, Suzuki Y, Kimura H, Nakauchi H, Suda T, Shinkai Y, Iwama A. Setdb1 maintains hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells by restricting the ectopic activation of non-hematopoietic genes. Blood. 128(5), pp638-49. 2016.
-
Yamashita M, Nitta E, Suda T. Regulation of hematopoietic stem cell integrity through p53 and its related factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1370(1), pp45-54. 2016.
-
仁田英里子,岩間厚志 造血幹細胞を制御する遺伝子1.ポリコーム遺伝子ほかエピジェネティクス制御遺伝子 造血器腫瘍アトラス第5版. p37-44. 2016 日本医事新報社
-
2015
-
Morikawa M, Yajima H, Nitta R, Inoue S, Ogura T, Sato C, Hirokawa N. X-ray and Cryo-EM Structures Reveal Mutual Conformational Changes of Kinesin and GTP-Microtubule upon binding. EMBO J. 2015 34:1270-86.
-
Yamashita M, Nitta E, Suda T. Maintenance of hematopoietic stem cell integrity and regulation of leukemogenesis by p53 and its coactivator Aspp1. Rinsho Ketsueki. 56(12), pp2426-33. 2015
-
Yamashita M, Nitta E* and Suda T.* Aspp1 preserves hematopoietic stem cell pool integrity and prevents malignant transformation. Cell Stem Cell. 17(1), pp23-34. 2015 (*corresponding authors)
-
仁田英里子,岩間厚志 The cancer stem cell model in hematological malignancies. 日本臨床 73(5), pp733-8. 2015.
-
仁田英里子,岩間厚志 骨髄の構造. Principles and practice 血液・造血器・リンパ系. p38-43. 2015 文光堂
-
Hirade Y, Kotoku N, Terasaka K, Saijo-Hamano Y, Fukumoto A, Mizukami H. Identification and functional analysis of 2-hydroxyflavanone C-glucosyltransferase in soybean (Glycine max) FEBS Lett. 2015, 589: 1778-1786.
-
2014
-
仁田亮 キネシン型分子モーターの構造変化と動作機構. 生物物理 (解説), 2014 54:133-9.
-
Inoue S, Nitta R, Hirokawa N. Crystal Structure of the KIF5C Motor Domain Without Any Nucleotide. Photon Factory Activity Report 2014 PART B #32.
-
Ogura T, Yajima H, Nitta R, Hirokawa N, Sato C. New Simulated Annealing Approach Considering Helix Bending Applied to Determine the 8.8 Å Structure of 15-Protofilament Microtubules. J. Struct. Biol. 2014 165-76. # Selected as a cover article.
-
Yunus J, Setsu T, Kikkawa S, Sakisaka T, Terashima T (2014) Cytoarchitecture of Olfactory Bulb in laggard Mutant Mouse. Neuroscience 275:259–271.
-
Nitta E and Iwama A. Diploid, not polyploid: new platelet producers. Blood. 124(17), pp2620-2. 2014
-
Cheong J-W, Nakamura-Ishizu A, Nitta E, Suda T Hematopoietic Stem Cell Aging and Oxidative Stress. Stem Cells: From Basic Research to Therapy: Basic Stem Cell Biology, Tissue Formation during Development, and Model Organisms. Vol.1, p88-107. 2014 CRC Press
-
Fukumura T, Furukawa Y, Kawaguchi T, Saijo-Hamano Y, Namba K, Imada K, Minamino T. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the periplasmic domain of FliP, an integral membrane component of the bacterial flagellar type III protein-export apparatus Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2014, F70: 1215-1218.
-
2013
-
Chang Q, Nitta R, Inoue S, Hirokawa N. Structural Basis for the ATP-induced Isomerization of Kinesin. J. Mol. Biol. 2013 425:1869-80.
-
Yamashita M, Nitta E*, Nagamatsu G, Ikushima YM, Hosokawa K, Arai F and Suda T.* Nucleostemin is indispensable for the maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells and genetic stability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441(1), pp196-201. 2013 (*corresponding authors)
-
Woon AP, Tohidpour A, Alonso H, Saijo-Hamano Y, Kwok T, Roujeinikova A. Conformational analysis of isolated domains of Helicobacter pylori CagA PLoS One. 2013, 8: e79367.
-
*Saijo-Hamano Y, Matsunami H, Namba K and Imada K. (*corresponding author) Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of a core fragment of FlgG, a bacterial flagellar rod protein Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2013, F69: 547-550.
-
(↑本稿のFlgG結晶の写真が世界結晶年である2014年初号表紙に採用されました http://journals.iucr.org/f/issues/2014/01/00/)
-
Martinez-Argudo I, Veenendaal AK, Liu X, Roehrich AD, Ronessen MC, Franzoni G, van Rietschoten KN, Morimoto YV, Saijo-Hamano Y, Avison MB, Studholme DJ, Namba K, Minamino T, Blocker AJ. Isolation of Salmonella mutants resistant to the inhibitory effect of Salicylidene acylhydrazides on flagella-mediated motility. PLoS One. 2013, 8: e52179.
-
2012
-
Nitta R, Hirokawa N. Fundamental Properties and Structure of Kinesin. Encyclopedia of Biophysics. Roberts, Gordon C.K. ed., Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. 2012. DOI:10.1007/978-3-642-16712-6.
-
Yajima H., #Ogura T, #Nitta R, Okada Y, Sato C, *Hirokawa N. Conformational Changes in Tubulin in GMPCPP and GDP-taxol Microtubules Observed by Cryo Electron Microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 2012 198:315-22. # Equal contribution. Faculty of 1000 Recommended Reading.
-
Imai H, Oomiya Y, Kikkawa S, Shoji W, Hibi M, Terashima T, Katsuyama Y (2012) Dynamic Changes in Gene Expression of Zebrafish Reelin Receptors during Embryogenesis and Hatching Period. Dev. Growth Diff. 54:253–263.
-
Bieniossek C, Imasaki T, Takagi Y & Berger I. MultiBac: Expanding the research toolbox for multiprotein complexes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 37, 49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.10.005. 2012.
-
Shimada M, Saijo-Hamano Y, Furukawa Y, Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K. Functional defect and restoration of temperature-sensitive mutants of FlhA, a subunit of the flagellar protein export apparatus. J Mol Biol. 2012, 415: 855-865.
-
2011
-
Nitta E, Yamashita M, Hosokawa K, Xian M, Takubo K, Arai F, Nakada S, Suda T. Telomerase reverse transcriptase protects ATM-deficient hematopoietic stem cells from ROS- induced apoptosis through a telomere independent mechanism. Blood. 117(16), pp4169-80. 2011 (*Plenary paper)
-
Yoshimi A, Goyama S, Watanabe-Okochi N, Yoshiki Y, Nannya Y, Nitta E, Arai S, Sato T, Shimabe M, Nakagawa M, Imai Y, Kitamura T, Kurokawa M. Evi1 represses PTEN expression and activates PI3K/AKT/mTOR via interactions with polycomb proteins. Blood. 117(13), pp3617-28. 2011
-
Imasaki T, Calero G, Cai G, Tsai KL, Yamada K, Cardelli F, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Berger I, Kornberg GL, Asturias FJ, Kornberg RD, Takagi Y. Architecture of the Mediator head module. Nature 475, 240–243. doi: 10.1038/nature10162. 2011.
-
Aydin I, Saijo-Hamano Y, Namba K, Thomas C, Roujeinikova A. Structural analysis of the essential resuscitation promoting factor YeaZ suggests a mechanism of nucleotide regulation through dimer reorganization. PLoS One. 2011, 6: e23245.
-
2010
-
廣川信隆, 仁田亮 生体分子モーター. 入門 構造生物学, 加藤龍一編 (分担執筆), 共立出版, 146-55, 2010. ISBN 978-4-320-05704-3
-
Kawaguchi K, Habara T, Terashima T, Kikkawa S (2010) GABA Modulates Development of Cerebellar Purkinje Cell Dendrites under Control of Endocannabinoid Signaling. J. Neurochem. 114:627–638
-
Kawaguchi K, Katsuyama Y, Kikkawa S, Setsu T, Terashima T (2010) PKH26 Is an Excellent Retrograde and Anterograde Fluorescent Tracer Characterized by a Small Injection Site and Strong Fluorescence Emission. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 73:65–72
-
Goyama S, Nitta E, Yoshino T, Kako S, Watanabe-Okochi N, Shimabe M, Imai Y, Takahashi K, Kurokawa M. EVI-1 interacts with histonemethyltransferases SUV39H1 and G9a for transcriptional repression and bone marrow immortalization. Leukemia. 24(1), pp81-8. 2010
-
Saijo-Hamano Y, Imada K, Minamino T, Kihara M, Shimada M, Kitao A, Namba K. Structure of the cytoplasmic domain of FlhA and implication for flagellar type III protein export. Mol Microbiol. 2010, 76: 260-268.
-
Minamino T, Shimada M, Okabe M, Saijo-Hamano Y, Imada K, Kihara M, Namba K. Role of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of FlhA in bacterial flagellar type III protein export. J Bacteriol. 2010, 192: 1929-1936.
-
2009
-
Hirokawa N, Nitta R, Okada Y. The mechanisms of kinesin motor motility: lessons from the monomeric motor KIF1A. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009 10:877-84.
-
仁田英里子,須田年生 白血病幹細胞の潮流Cancer stem cell concepts—lesson from leukemia. 日本臨床 67(10),pp1863-7.2009
-
仁田英里子,須田年生 幹細胞における老化とがんの制御機構—Aging and cancer in hematopoietic stem cells—. 日本老年医科学雑誌 46(3), pp195-9. 2009
-
2008
-
Nitta R, Hirokawa N. Structural Mechanism of the Microtubule-Activated Nucleotide Exchange of Molecular Motor Kinesin. Photon Factory Activity Report 2008 PART A: Highlights;56-57.
-
Nitta R, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. Crystallization of the Mg-releasing intermediates of kinesin ATPase. Nat. protoc. 2008;DOI:10.1038/nprot.2008. 239.
-
Nitta R, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. Structural model for strain-dependent microtubule activation of Mg-ADP release from kinesin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008 15:1067-75.
-
Sato T, Goyama S, Nitta E, Takeshita M, Yoshimi M, Nakagawa M,Kawazu M,Ichikawa M,Kurokawa M. Evi-1 promotes para-aortic splanchnopleural hematopoiesis through up-regulation of GATA-2 and repression of TGF-β signaling. Cancer Science. 99(7), pp1407-13. 2008
-
Matsuoka S, Oike Y, Onoyama I, Iwama A, Arai F, Takubo K, Mashimo Y, Oguro H, Nitta E, Ito K, Miyamoto K, Yoshihara H, Hosokawa K, Nakamura Y, Gomei Y, Iwasaki H, Hayashi Y, Matsuzaki Y, Nakayama K, Ikeda Y, Hata A, Chiba S, Nakayama KI, Suda T. Fbxw7 acts as a critical fail-safe against premature loss of hematopoietic stem cells and development of T-ALL. Genes Dev. 22(8), pp986-991. 2008
-
Takeshita M, Ichikawa M, Nitta E, Goyama S, Asai T, Ogawa S, Chiba S, Kurokawa M. AML1-Evi-1 specifically transforms hematopoietic stem cells through fusion of the entire Evi-1 sequence to AML1. Leukemia. 22(6):1241-9. 2008
-
2007
-
Shibata-Iwasaki R, Dekimoto H, Katsuyama Y, Kikkawa S, Terashima T (2007) Anterograde Labeling of Corticospinal Tract in jimpy Mutant Mice by DiI Injection into Motor Cortex. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 70:297–301
-
Muraoka D, Katsuyama Y, Kikkawa S, Terashima T (2007) Postnatal Development of Entorhinodentate Projection of Reeler Mutant Mouse. Dev. Neurosci. 29:59–72
-
Katsuyama Y, Oomiya Y, Dekimoto H, Motooka E, Takano A, Kikkawa S, Hibi M, Terashima T (2007) Expression of Zebrafish ROR alpha Gene in Cerebellar-like Structures. Dev. Dyn. 236:2694–2701
-
Nitta E, Izutsu K, Sato T, Ota Y, Takeuchi K, Kamijo A, Takahashi K, Oshima K, Kanda Y, Chiba S, Motokura T, Kurokawa M. A high incidence of late-onset neutropenia following rituximab-containing chemotherapy as a primary treatment of CD20-positive B-cell lymphoma: a single-institution study. Ann Oncol. 18(2):364-9. 2007
-
2005
-
Taylor MR, Kikkawa S, Diez-Juan A, Ramamurthy V, Kawakami K, Carmeliet P, Brockerhoff SE (2005) The Zebrafish pob Gene Entodes a Novel Protein Required for Survival of Red Cone Photoreceptor Cells. Genetics 170:263–273
-
Nitta E, Izutsu K, Yamaguchi Y, Imai Y, Ogawa S, Chiba S, Kurokawa M, Hirai H. Oligomerization of Evi-1 regulated by the PR domain contributes to recruitment of corepressor CtBP. Oncogene. 24(40), pp6165-73. 2005
-
Ogawa T, Nitta R, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. A Common Mechanism for Microtubule Destabilizers- M Type Kinesins Stabilize Curling of the Protofilament Using the Class-Specific Neck and Loops. Cell 2004 116:591-602. #Faculty of 1000 Recommended Reading.
-
Saijo-Hamano Y, Imada K, Minamino T, Kihara M, Macnab RM, Namba K. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of FlhA, a membrane-protein subunit of the bacterial flagellar type III protein-export apparatus. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2005, 61: 599-602.
-
2004
-
Nitta R, Kikkawa M, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. KIF1A alternately uses two loops to bind microtubules. Science 2004 305:678-83.
-
Misaki K, Kikkawa S, Terashima T (2004) Reelin-expressing Neurons in the Anterior Commissure and Corpus Callosum of the Rat. Dev. Brain Res. 148:89–96
-
Yamaguchi Y, Kurokawa M, Imai Y, Izutsu K, Asai T, Ichikawa M, Yamamoto G, Nitta E, Yamagata T, Sasaki K, Mitani K, Ogawa S, Chiba S, Hirai H. AML1 is functionally regulated through p300-mediated acetylation on specific lysine residues. J Biol Chem. 279(15):15630-8. 2004
-
Imai Y, Kurokawa M, Yamaguchi Y, Izutsu K, Nitta E, Mitani K, Satake M, Noda T, Ito Y, Hirai H. The corepressor mSin3A regulates phosphorylation-induced activation, intranuclear location, and stability of AML1. Mol Cell Biol. 24(3):1033-43. 2004
-
Saijo-Hamano Y, Minamino T, Macnab RM, Namba K. Structural and functional analysis of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of FlhA, an integral membrane component of the type III flagellar protein export apparatus in Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 2004, 343: 457-66.
-
Saijo-Hamano Y, Minamino T, Macnab RM, Namba K. "Structural and functional analysis of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of FlhA, an integral membrane component of the type III flagellar protein export apparatus in Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 2004, 343: 457-66.
-
Minamino T, Saijo-Hamano Y, Furukawa Y, González-Pedrajo B, Macnab RM, Namba K. Domain organization and function of Salmonella FliK, a flagellar hook-length control protein. J Mol Biol. 2004, 341: 491-502.
-
Saijo-Hamano Y, Uchida N, Namba K, Oosawa K. In vitro characterization of FlgB, FlgC, FlgF, FlgG, and FliE, flagellar basal body proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 2004, 339: 423-435.
-
2003
-
Nitta R, Ogawa T, Kikkawa M, Okada Y, Hirokawa N. X-ray crystallography of kinesin motors. Photon Factory Activity Report 2003 PART A: Highlights;29-31.
-
Kikkawa S, Yamamoto T, Misaki K, Ikeda Y, Okado H, Ogawa M, Woodhams PL, Terashima T (2003) Missplicing Resulting from a Short Deletion in the Reelin Gene Causes Reeler-like Neuronal Disorders in the Mutant Shaking Rat Kawasaki. J. Comp. Neurol. 463:303–315
-
- 2002
-
Ohkubo N, Lee YD, Morishima A, Terashima T, Kikkawa S, Tohyama M, Sakanaka M, Tanaka J, Maeda N, Vitek MP, Mitsuda N (2002) Apolipoprotein E and Reelin Ligands Modulate Tau Phosphorylation through an Apolipoprotein E Receptor/Disabled-1/Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Cascade. FASEB J. 17:295–297
-
Rina-Susilowati, Jusuf AA, Sakagami H, Kikkawa S, Kondo H, Minami Y, Terashima T (2001) Distribution of Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase I Beta 2 in the Central Nervous System of the Rat. Brain Res. 911:1–11
-
若海美智, 志賀剛, 鈴木豪, 保坂文駿, 仁田亮, 佐藤太彦, 今村仁治, 松田直樹, 笠貫宏, 土谷隆紀, 西方かおり, 長沼美代子 アミオダロン経口投与導入時の初期投与量の検討(第2報). 臨床薬理 2000;31:407-8.
-
Iwasa T, Yanai T, Nakagawa M, Kikkawa S, Obata S, Usukura J, Tsuda M (2000) G Protein α Subunit Genes in Octopus Photoreceptor Cells. Zool. Sci. 17:711–716
-
Saijo-Hamano Y, Namba K, Oosawa K. A new purification method for overproduced proteins sensitive to endogenous proteases. J Struct Biol. 2000, 132: 142-146.
-
寺島俊雄,薛 富義,吉川知志,池田やよい (1999) リーラーマウス顔面神経核の細胞構築,解剖学雑誌 74:411–20
-
寺島俊雄,吉川知志 (1999) マウス大脳皮質の形成異常 —リーラーマウスを中心に —,脳の科学 21:1319–1324
-
Nakagawa M, Iwasa T, Kikkawa S, Tsuda M, Ebrey TG (1999) How Vertebrate and Invertebrate Visual Pigments Differ in their Mechanism of Photoactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:6189–6192
-
Nitta R, Sakomura Y, Tanimoto K, Hidai T, Kasanuki H, Aomi S, Nishikawa T. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma of the right atrium undiagnosed by transvenous endocardial tumor biopsy. Intern. Med. 1998 37:1023-6.
-
Kikkawa S, Yoshida N, Nakagawa M, Iwasa T, Tsuda M (1998) A Novel Rhodopsin Kinase in Octopus Photoreceptor Possesses a Pleckstrin Homology Domain and Is Activated by G Protein βγ-Subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 273:7441–7447
-
Nakagawa M, Kikkawa S, Tominaga K, Tsugi N, Tsuda M (1998) A Novel Photointermediate of Octopus Rhodopsin Activates Its G-protein FEBS Lett. 436:259–262
-
Iwasa T, Colmenares LU, Hirata K, Arime Y, Nakagawa M, Kikkawa S, Takashima H, Nosaka A, Naito A, Saito H, Liu RSH, Tsuda M (1998) 19F NMR and UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopic Studies of Fluorinated Octopus Rhodopsin and Its Photoproducts. J. Phys. Chem. A 102:5602–5610
-
吉川知志,中川将司 (1997) トランスデューサー;情報変換分子Gタンパク質,「知覚のセンサー;生物の巧みなシグナルの獲得」,津田基之 編,吉岡書店 pp. 15–23
-
Nakagawa M, Kikkawa S, Iwasa T, Tsuda M (1997) Light-induced Protein Conformational Changes in the Photolysis of Octopus Rhodopsin. Biophys. J. 72:2320–2328
-
Nakagawa M, Iwasa T, Kikkawa S, Takao T, Shimonishi Y, Tsuda M (1997) Identification of Two Palmitoyl Groups in Octopus Rhodopsin. Photochem. Photobiol. 65:185–189
-
Saijo Y, Takeda S, Scherer A, Kobayashi T, Maéda Y, Taniguchi H, Yao M, Wakatsuki S. Production, crystallization, and preliminary X-ray analysis of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin complex consisting of troponin C and fragment (1-47) of troponin I. Protein Sci. 1997, 6: 916-918.
-
津田基之,岩佐達郎,中川将司,吉川知志 (1996) タンパク質超分子システムの構造と機能,「新タンパク質応用工学」,籏野昌弘 編,フィジテクノシステム pp. 290–295
-
Kikkawa S, Tominaga K, Nakagawa M, Iwasa T, Tsuda M (1996) Simple Purification and Functional Reconstitution of Octopus Photoreceptor Gq Which Couples Rhodopsin To Phospholipase C. Biochemistry 35:15857–15864
-
Kikkawa S, Nakagawa M, Iwasa T, Kaneko A, Tsuda M (1993) GTP-binding Protein Couples with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor in Bovine Retinal On-bipolar Cell. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 195:374–379
-
Tsuda M, Iwasa T, Nakagawa M, Kikkawa S, Tsuda T (1993) Regulaion of signal coupling proteins in octopus photoreceptors. in “Frontiers of Photobiology” Eds. Shima A et al., Elsevier Science Publishers pp. 189–194
-
Tsuda M, Nakagawa M, Iwasa T, Kikkawa S (1992) Light induced conformational changes of octopus rhodopsin. in “Structures and Functions of Retinal Proteins” Ed. Rigaud JL, John Libbey Eurotext Ltd. pp. 287–290
-
津田基之,岩佐達郎,中川将司,吉川知志 (1992) 光センサーロドプシンの機能,電子写真 31:572–577
-
Kikkawa S, Takahashi K, Takahashi K, Shimada N, Ui M, Kimura N, Katada T (1992) Activation of Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase by Mastoparan a Peptide Isolated from Wasp Venom FEBS Lett. 305:237–240
-
Kikkawa S, Takahashi K, Takahashi K, Shimada N, Ui M, Kimura N, Katada T (1990) Conversion of GDP into GTP by Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase on GTP-binding Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 265:21536–21540
-
Hoshino S, Kikkawa S, Takahashi K, Itoh H, Kaziro Y, Kawasaki H, Suzuki K, Katada T, Ui M (1990) Identification of Sites for Alkylation by N-Ethylmaleimide and Pertussis Toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation on GTP-binding Proteins. FEBS Lett. 276:227–231
-
Kikkawa S, Takahashi K, Katada T, Inada Y (1989) Esterification of Chiral Secondary Alcohols with Fatty-acid in Organic Solvents by Polyethylene Glycol-modified Lipase. Biochem. Int. 19:1125–1131
-
Kobayashi I, Shibasaki H, Takahashi K, Kikkawa S, Ui M, Katada T (1989) Purification of GTP-binding Proteins from Bovine Brain Membranes – Identification of Heterogeneity of α-Subunit of Go Proteins. FEBS Lett. 257:177–180
-
大和田きみ子,吉川知志,高橋勝宣 (1988) 酵素蛋白質の有機溶媒可溶化と磁性化,化学と生物 26:454–455